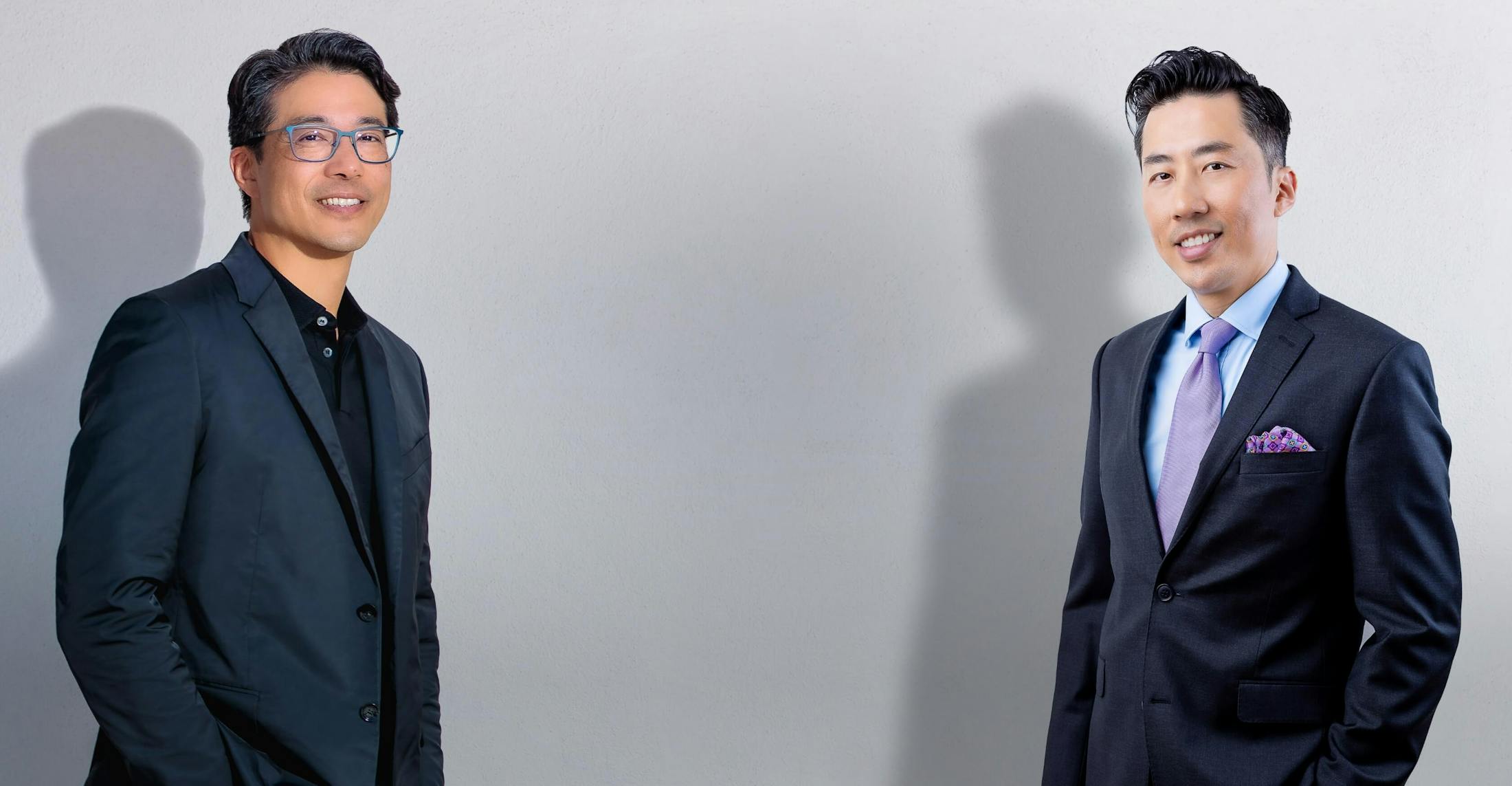
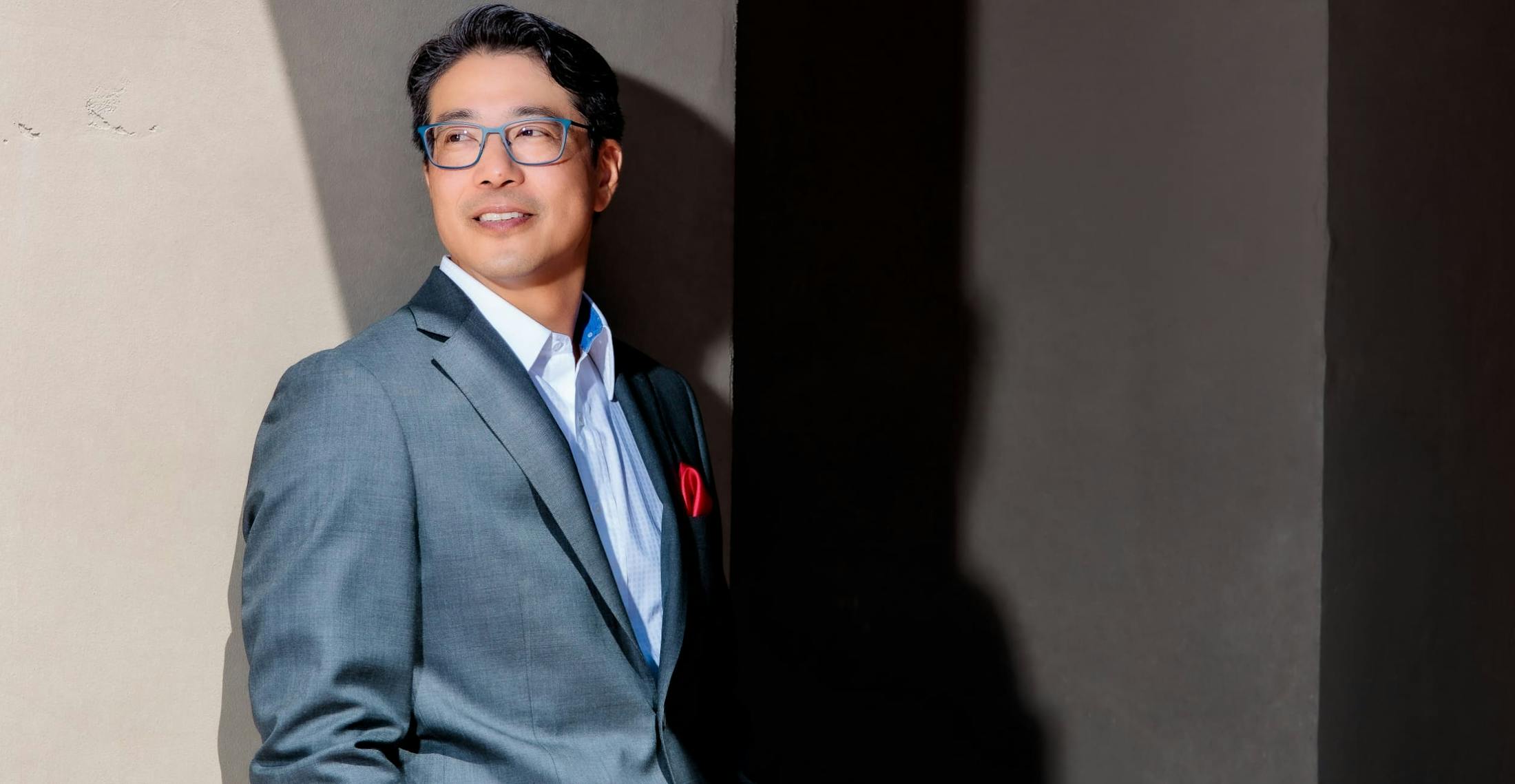
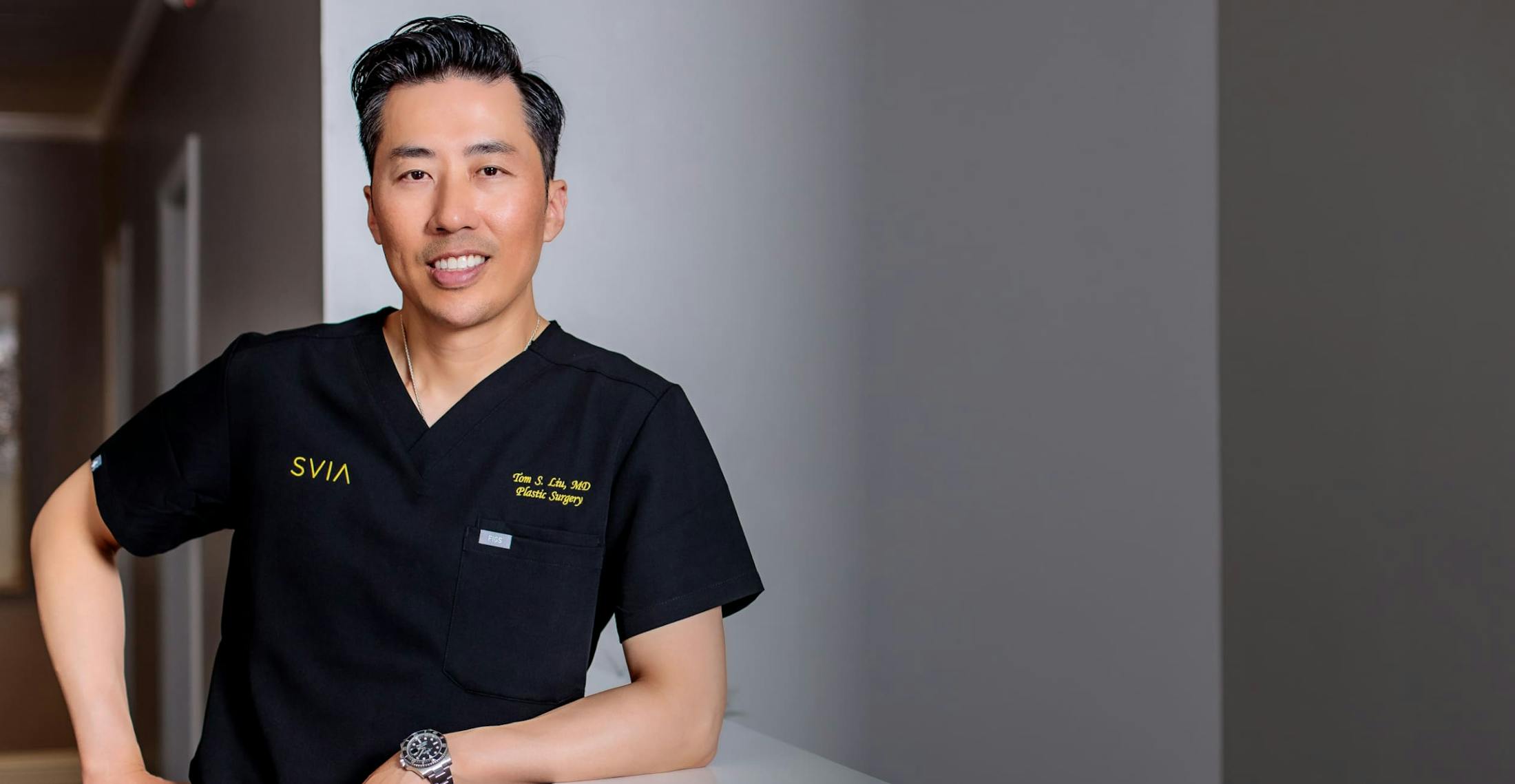
Board-Certified Plastic Surgeon JEROME H. LIU, MD. MSHS
After discovering his passion for cosmetic surgery at a relatively early age, Dr. Liu went on to complete his medical education at UCLA's David Geffen School of Medicine, earning some of the highest possible honors. His talent and expertise has only been enhanced by his ability to study under some of the industry's most respected luminaries.
Meet Dr. Jerome Liu